What are the features of SAS business intelligence? This topic unveils a pivotal tool that modern organizations utilize to harness data for strategic advantage. SAS Business Intelligence stands out by enabling organizations to transform data into actionable insights, thereby optimizing decision-making processes and enhancing operational efficiency.
In today’s data-driven environment, SAS Business Intelligence serves as a cornerstone for companies seeking to gain a competitive edge. Its significance extends across various industries, targeting professionals who rely on data analytics to inform their strategies and actions. By understanding the core features of SAS, one can appreciate how it empowers users to visualize data, generate comprehensive reports, and conduct in-depth analyses.
Overview of SAS Business Intelligence
SAS Business Intelligence (BI) provides organizations with the essential tools needed to convert data into actionable insights. In today’s data-driven landscape, leveraging advanced analytics and comprehensive reporting capabilities is crucial for making informed decisions that drive growth and efficiency. SAS BI empowers businesses to harness their data effectively, enabling strategic planning and operational improvement.The primary objectives of utilizing SAS for business intelligence include enhancing data visualization, improving decision-making processes, and fostering a culture of analytics within organizations.
By offering powerful forecasting, reporting, and data exploration features, SAS BI helps organizations to identify trends, optimize resources, and elevate overall performance.
Target Audience and Beneficial Industries
SAS Business Intelligence is designed for a diverse array of industries and roles that require data analysis and reporting capabilities. The following sectors particularly benefit from SAS solutions:
- Financial Services: Financial institutions utilize SAS for risk management, fraud detection, and regulatory compliance. These capabilities ensure that data-driven decisions align with market trends and regulatory requirements.
- Healthcare: Healthcare organizations leverage SAS BI to improve patient outcomes through data analysis, operational efficiency, and cost management. Predictive analytics facilitates better resource allocation and enhances care quality.
- Retail: Retailers use SAS to analyze consumer behavior, optimize supply chains, and enhance customer experiences. This data-centric approach supports inventory management and targeted marketing strategies.
- Manufacturing: The manufacturing sector applies SAS solutions to streamline production processes, enhance quality control, and reduce waste. By tapping into IoT data, manufacturers can also predict maintenance needs and optimize operations.
- Telecommunications: Telecommunications companies adopt SAS for customer segmentation, churn analysis, and network optimization. This enables improved customer retention and service delivery.
In summary, SAS Business Intelligence serves a broad audience, including data analysts, business strategists, and executives across various industries. With its robust capabilities, SAS BI stands as a cornerstone for organizations aiming to thrive in a competitive environment.
Key Features of SAS Business Intelligence

SAS Business Intelligence software is designed to provide organizations with comprehensive tools for data analysis, reporting, and visualization. Its robust functionality enables businesses to convert data into actionable insights, thereby driving informed decision-making and strategic planning. Below are some of the core features that distinguish SAS Business Intelligence in the market.
Data Visualization
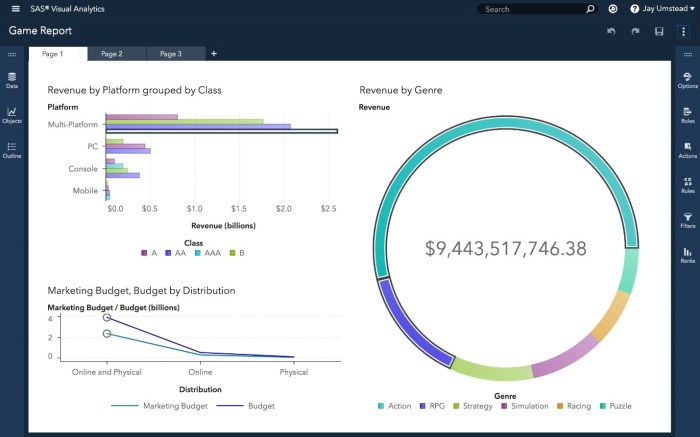
Data visualization is a fundamental aspect of SAS Business Intelligence, allowing users to represent complex data sets graphically. This feature is crucial for identifying trends, patterns, and outliers in data which may not be immediately apparent through traditional analysis methods. SAS provides a variety of visualization options such as graphs, charts, and dashboards that are customizable to meet specific reporting needs.
- Interactive Dashboards: Users can create interactive and dynamic dashboards that provide real-time data monitoring. For instance, a sales manager can visualize sales performance metrics across different regions, enabling quick assessment of market trends.
- Customizable Reports: SAS allows users to design reports tailored to their audience with a range of visualization styles. A financial analyst might generate a report illustrating monthly expenditure vs. budget using bar graphs to highlight discrepancies effectively.
- Geospatial Mapping: The ability to visualize data on maps enhances geographical insights. A logistics company can leverage this feature to optimize delivery routes based on geographic sales data.
Reporting Capabilities
SAS Business Intelligence excels in its reporting capabilities, providing users with tools to create comprehensive reports that facilitate performance monitoring and compliance audits. These reports can be generated on-demand or scheduled for regular distribution.
- Automated Reporting: SAS enables automation of routine reports, allowing stakeholders to receive timely information without manual intervention. For example, a marketing team can set up weekly reports to evaluate campaign performance automatically.
- Ad-Hoc Reporting: Users can generate reports spontaneously to address immediate business questions. A project manager might require a detailed report on project costs at any point during the project lifecycle.
- Multi-format Export Options: Reports can be exported in various formats such as PDF, Excel, and HTML, ensuring compatibility with different organizational needs. This flexibility is essential for compliance and presentation purposes.
Analytics Functionality, What are the features of SAS business intelligence?
The analytical capabilities of SAS Business Intelligence are robust, providing users with the ability to conduct in-depth analysis using advanced statistical methods and predictive analytics. This feature empowers organizations to make data-driven decisions based on historical data trends.
- Predictive Analytics: SAS includes predictive modeling tools that help organizations forecast future trends. For example, a retail company can analyze past sales data to predict future inventory needs, thereby minimizing stock outages.
- Statistical Analysis Tools: SAS offers a suite of statistical functions that facilitate sophisticated data analysis. A healthcare provider can use these tools to analyze patient data for identifying factors affecting treatment outcomes.
- Data Mining Capabilities: Users can discover patterns in large datasets through data mining techniques. A financial institution may use this feature to detect fraudulent transactions by recognizing unusual behavior patterns.
Integration Capabilities of SAS Business Intelligence
SAS Business Intelligence stands out in the analytics landscape due to its robust integration capabilities that empower organizations to unify data from various sources. This flexibility allows businesses to leverage existing data assets, enhancing their analytical processes and reporting capabilities. The integration framework provided by SAS ensures seamless connectivity with diverse data sources, enabling a comprehensive view of organizational performance.
Data Source Integration
SAS supports integration with a wide range of data sources, including databases, data warehouses, and external applications. This multi-faceted connectivity is crucial for organizations looking to consolidate their data for enhanced analytical insights. Key integration features include:
- Database Connectivity: SAS supports numerous databases such as Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, and IBM Db2, allowing organizations to extract and manipulate data directly.
- Data Virtualization: This feature enables real-time access to diverse data sources without the need to replicate data, streamlining the integration process.
- ODBC and JDBC Support: SAS provides ODBC and JDBC drivers, facilitating connections to various relational database management systems (RDBMS) for efficient data retrieval.
Cloud Services and Database Connectivity
With the growing prevalence of cloud computing, SAS Business Intelligence has adapted to connect seamlessly with various cloud services. This connectivity offers organizations the flexibility to leverage cloud-based data storage and analytics solutions effectively:
- Integration with Cloud Providers: SAS can connect to major cloud platforms, including Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform, allowing businesses to harness cloud capabilities for their analytical needs.
- REST APIs: SAS utilizes REST APIs for integration with cloud applications, facilitating the exchange of data between SAS and cloud-based services.
- Direct Access to Cloud Databases: SAS can directly connect to cloud databases such as Amazon Redshift and Snowflake, enabling quick access to large datasets stored in the cloud.
Comparison with Competitors
When evaluating SAS’s integration capabilities, it is beneficial to compare these with other leading business intelligence solutions in the market. SAS offers several advantages:
- Versatility: SAS provides extensive integration options that surpass many competitors, allowing for a wider range of data sources.
- Data Management Features: Unlike many other platforms, SAS includes robust data management capabilities that facilitate data cleansing and preparation as part of the integration process.
- Comprehensive Documentation: SAS offers thorough documentation and support for integration processes, enhancing user experience compared to some competitors that may lack in this area.
“The ability to integrate seamlessly with various data sources is a defining feature of SAS Business Intelligence, enabling organizations to maximize their data potential.”
User Experience and Interface of SAS Business Intelligence: What Are The Features Of SAS Business Intelligence?
The user experience and interface of SAS Business Intelligence (BI) are crucial elements that significantly enhance the effectiveness of data analysis and reporting. A well-designed interface not only promotes productivity but also empowers users of varying skill levels to engage with data seamlessly. In this section, we will delve into the interface design, its usability impacts, and the feedback gathered from users regarding their experiences with the SAS BI platform.
User Interface Design and Usability Impact
The user interface of SAS Business Intelligence is intuitively designed to facilitate a smooth interaction between users and the software. Key aspects of the design include:
- Intuitive Layout: The interface is structured to present tools and features in a logical order, allowing users to navigate through reports and dashboards effortlessly.
- Customizable Dashboards: Users can tailor their dashboards to display the metrics and visualizations that matter most to them, enhancing relevance and focus.
- Responsive Design: The interface adapts to various devices, ensuring that users can access their data and perform analyses whether they are on a desktop or mobile device.
The overall impact of these design features leads to a more engaging experience, reducing the learning curve associated with utilizing complex data analytics tools.
Accessibility for Various User Skill Levels
SAS Business Intelligence prioritizes accessibility across different user skill levels, ensuring that both novice and experienced users can derive value from the platform. SAS incorporates various features to support this goal:
- Interactive Tutorials: Comprehensive tutorials guide new users through the essential functionalities of the software, fostering confidence in navigating the platform.
- Role-Based Access: Users can access features and tools specific to their roles, which streamlines the experience and minimizes confusion.
- Help Documentation: Extensive documentation is readily available, allowing users to seek assistance on demand, thus promoting self-learning.
By considering different levels of expertise, SAS ensures that its BI solutions are inclusive and accessible to a broader audience.
User Feedback on the SAS Business Intelligence Interface
User feedback plays a vital role in shaping the continuous improvement of the SAS Business Intelligence interface. Users have expressed their experiences, highlighting both strengths and areas for enhancement:
- Positive Feedback: Many users appreciate the clean design and ease of use, noting that the interface allows them to quickly generate insights without extensive training.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Users often mention the collaborative features that enable teams to work together efficiently, sharing dashboards and reports seamlessly.
- Areas for Improvement: Some feedback indicates a desire for more advanced analytical tools to be integrated directly into the primary interface, enabling users to perform deeper analyses without switching contexts.
This feedback loop ensures that SAS continues to refine its offerings, catering to the evolving needs of its user base and enhancing the overall user experience with the Business Intelligence platform.