SAS business intelligence case studies in various industries. serve as a critical gateway to understanding the transformative power of data analytics across different sectors. These case studies highlight the innovative ways organizations harness SAS technology to enhance operational efficiency, improve customer satisfaction, and drive strategic decision-making. By exploring the unique applications within healthcare, retail, financial services, and more, we can appreciate the pivotal role SAS plays in shaping modern business strategies and outcomes.
In this exploration, we will delve into specific examples that showcase the successful implementation of SAS solutions. From healthcare transformations that enhance patient care to retail innovations that streamline inventory management and customer insights, these case studies illuminate the practical benefits of SAS business intelligence. Furthermore, we will address the challenges faced during these implementations, providing a well-rounded perspective on the journey toward effective data utilization.
Industry-Specific Applications of SAS Business Intelligence
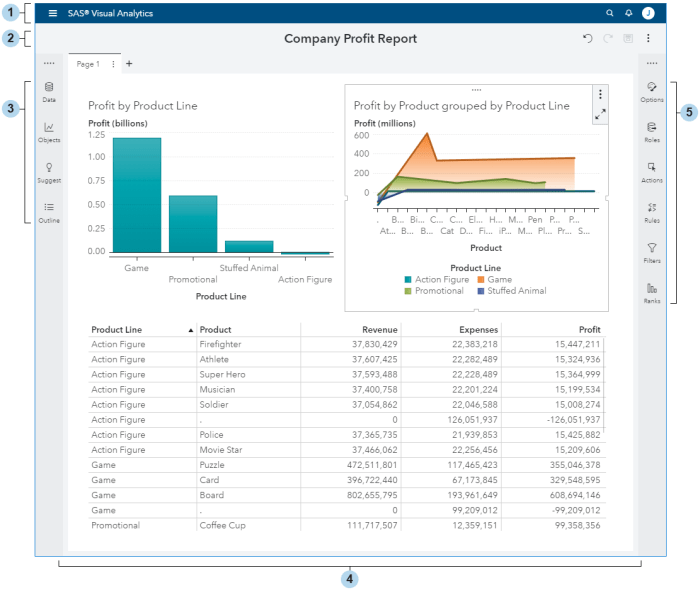
SAS Business Intelligence has become a vital asset across various industries, enhancing operational efficiency and decision-making processes. By leveraging advanced analytics, organizations can gain valuable insights tailored to their specific sector needs. Below are detailed applications of SAS in healthcare, retail, and financial services, highlighting its transformative impact.
Healthcare Sector Implementation
In the healthcare industry, SAS Business Intelligence plays a crucial role in improving patient care and operational efficiency. Through data integration and predictive analytics, healthcare providers can enhance treatment outcomes and streamline processes. Some specific applications include:
- Patient Outcome Prediction: By analyzing historical patient data, SAS can predict outcomes for various treatments, enabling personalized care plans.
- Operational Efficiency: SAS tools assist hospitals in optimizing resource allocation, reducing wait times, and lowering costs through effective staffing and scheduling.
- Clinical Research: SAS supports clinical trials with robust data analysis capabilities, ensuring compliance and accuracy in reporting results.
“Utilizing SAS analytics allows healthcare organizations to transition from reactive to proactive patient care, thus enhancing overall quality.”
Retail Applications for Inventory Management and Customer Analytics
In the retail sector, SAS Business Intelligence enables organizations to manage inventory effectively and understand customer behavior. This understanding is crucial for maintaining competitiveness and maximizing sales. Key applications include:
- Inventory Optimization: SAS provides real-time inventory tracking and demand forecasting, helping retailers reduce excess stock and avoid stockouts.
- Customer Segmentation: By analyzing purchasing patterns, retailers can segment customers, allowing for targeted marketing strategies and personalized promotions.
- Sales Forecasting: SAS’s predictive analytics aids in anticipating future sales trends, ensuring that product availability meets consumer demand.
“The integration of SAS analytics in retail not only enhances operational efficiency but also enriches the customer shopping experience.”
Financial Services Role in Risk Management and Fraud Detection
In financial services, the implementation of SAS Business Intelligence is pivotal for effective risk management and fraud detection. Financial institutions leverage SAS analytics to safeguard assets and enhance regulatory compliance. Applications include:
- Risk Assessment: SAS tools help quantify risk exposure across various portfolios, enabling financial institutions to make informed investment decisions.
- Fraud Detection: Utilizing real-time analytics, SAS identifies unusual transaction patterns, providing alerts that help prevent potential fraud.
- Regulatory Compliance: SAS solutions ensure compliance with financial regulations by streamlining reporting processes and maintaining data integrity.
“Employing SAS analytics for risk management and fraud detection strengthens the integrity of financial institutions in a rapidly evolving landscape.”
Case Studies of Successful SAS Implementations
SAS Business Intelligence has consistently demonstrated its potential to transform operations across various industries. By leveraging advanced analytics, organizations have achieved significant improvements in efficiency, decision-making, and customer satisfaction. This segment delves into specific case studies that showcase successful implementations of SAS in the manufacturing, logistics, and telecommunications sectors.
Successful SAS Project in the Manufacturing Industry, SAS business intelligence case studies in various industries.
One notable example of SAS implementation in the manufacturing industry is a leading automotive company that faced challenges in production efficiency and quality control. By integrating SAS Analytics, they were able to analyze vast amounts of production data in real time. The implementation involved:
- Data integration from multiple sources, including sensors on production lines, to monitor real-time operations.
- Predictive analytics to forecast potential machinery failures, thereby reducing downtime.
- Use of visualization tools to identify bottlenecks and optimize workflow processes.
As a result, the company achieved a 20% increase in overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) and a 15% reduction in manufacturing defects, significantly enhancing product quality and operational efficiency.
Operational Efficiency Improvement in a Logistics Company
A case study involving a global logistics provider illustrates how SAS can enhance operational efficiency. The company sought to streamline its supply chain operations to respond faster to market changes and customer demands. Through SAS’s data-driven insights, the logistics company was able to:
- Develop a comprehensive dashboard that provided real-time visibility into shipment statuses and delivery metrics.
- Utilize advanced route optimization algorithms to minimize transportation costs and improve delivery speed.
- Implement demand forecasting models to better align inventory levels with customer needs.
These initiatives resulted in a 30% reduction in transportation costs and improved on-time delivery performance by 25%, thus elevating customer satisfaction levels.
Enhanced Customer Experience in the Telecommunications Sector
In the telecommunications sector, a prominent service provider adopted SAS to enhance customer experience and retention rates. This project focused on understanding customer behaviors and preferences through extensive data analytics. Key components of the project included:
- Customer segmentation analysis to tailor marketing campaigns and service offerings based on individual preferences.
- Implementation of churn prediction models that identified at-risk customers, allowing for proactive retention strategies.
- Use of sentiment analysis on customer feedback to improve service quality and address issues swiftly.
The outcome was a notable increase in customer retention by 18% and a significant boost in net promoter score (NPS), reflecting improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Challenges Faced When Implementing SAS Business Intelligence
The adoption of SAS Business Intelligence solutions presents numerous opportunities, but organizations often encounter significant challenges during implementation. Understanding these challenges is crucial for successful integration and maximizing the benefits of SAS tools.Data quality issues can severely impact the effectiveness of SAS implementations. Organizations frequently struggle with inconsistent, incomplete, or inaccurate data, which undermines decision-making processes. The following points highlight the implications of poor data quality on SAS deployment:
- Inaccurate Analysis: If the underlying data is flawed, the analytics generated will not provide reliable insights, leading to misguided strategies and decisions.
- Increased Costs: Time and resources are wasted in attempts to clean and validate data, diverting attention from more strategic tasks.
- User Trust: Users that encounter discrepancies in data are less likely to trust the reports generated, which can lead to resistance in adopting the new system.
Resistance to Change Among Staff
Resistance to change is a common barrier that organizations face when deploying SAS Business Intelligence solutions. Employees may feel threatened by new technologies or uncertain about their ability to adapt, which can hinder the implementation process. Key factors contributing to this resistance include:
- Lack of Training: Insufficient training can leave staff feeling unprepared to utilize SAS tools effectively, increasing anxiety and resistance.
- Fear of Job Loss: Employees may fear that automation and analytics will render their positions obsolete, leading to pushback against the new systems.
- Established Workflows: Existing processes may be deeply ingrained in the organizational culture, making it difficult to transition to new methodologies.
Addressing these challenges requires a proactive approach, including investing in robust data governance strategies and fostering a culture of continuous learning and adaptation. By recognizing and mitigating these potential hurdles, organizations can enhance the effectiveness of their SAS Business Intelligence implementations and achieve their analytical goals more efficiently.
Future Trends in SAS Business Intelligence Across Industries: SAS Business Intelligence Case Studies In Various Industries.
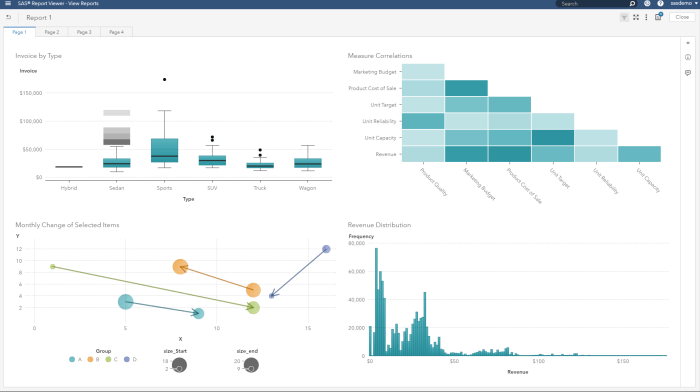
The future of SAS Business Intelligence (BI) is poised for significant transformation as emerging technologies and innovations take center stage. Organizations across various sectors are continually seeking ways to leverage data for strategic decision-making and operational efficiency. As these advancements unfold, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and big data analytics will redefine how businesses utilize SAS BI tools to gain insights.Emerging technologies, such as cloud computing, the Internet of Things (IoT), and advanced data visualization tools, are set to influence the landscape of SAS Business Intelligence.
These technologies not only enhance the accessibility and speed of data processing but also enable organizations to harness vast amounts of data generated from diverse sources. As a result, businesses can gain real-time insights, drive customer engagement, and optimize operations across multiple industries.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence in SAS Applications
The incorporation of artificial intelligence into SAS applications is transforming analytical capabilities and enhancing decision-making processes. AI enables SAS to process and analyze massive datasets at unprecedented speeds, allowing businesses to uncover patterns and trends that were previously unattainable.Key aspects of AI integration in SAS applications include:
- Predictive Analytics: AI-driven algorithms provide businesses with predictive insights, helping them anticipate market trends and customer behaviors. For example, retail companies can optimize inventory management by predicting demand based on consumer purchasing patterns.
- Natural Language Processing: Integrating natural language processing into SAS applications allows users to query data using conversational language, making data analysis more accessible to non-technical users.
- Automated Reporting: AI capabilities facilitate automated report generation, enabling organizations to save time and enhance accuracy in the reporting process.
The evolution of AI in SAS BI applications indicates a future where organizations can leverage sophisticated algorithms to drive precise business strategies and enhance operational efficiencies.
Evolution of SAS Capabilities for Big Data Analytics
As data volumes continue to grow exponentially, the capabilities of SAS in big data analytics are expected to evolve significantly. The integration of advanced analytics tools and machine learning capabilities will empower organizations to analyze complex datasets more effectively.Future trends in SAS’s big data capabilities include:
- Enhanced Data Integration: SAS will likely evolve to provide more robust data integration tools that can seamlessly connect with various data sources, including cloud-based platforms and real-time data streams from IoT devices.
- Real-Time Analytics: The demand for real-time analytics will drive SAS to enhance its ability to process data instantaneously, allowing businesses to make decisions based on the most current information available.
- Augmented Analytics: The rise of augmented analytics will support users in discovering insights with minimal manual intervention, leveraging machine learning to automate data preparation and analysis.
The continuous advancement in big data analytics capabilities will enable organizations to gain deeper insights, drive innovation, and maintain a competitive edge in their respective industries.