Key metrics to track in SAS business intelligence projects. These metrics play a crucial role in guiding strategic decisions and enhancing operational efficiency within organizations. By closely monitoring specific metrics, businesses can better understand their performance, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions that drive success. Various organizations have harnessed the power of key metrics, leading to tangible results in their SAS BI initiatives.
The importance of these metrics cannot be overstated, as they encompass a range of categories, including performance, operational, and financial metrics, each contributing uniquely to the overall business intelligence landscape. Understanding the nuances between quantitative and qualitative metrics further enriches the analytical capabilities of SAS projects, ensuring comprehensive insights are derived from the data.
Importance of Key Metrics in Business Intelligence: Key Metrics To Track In SAS Business Intelligence Projects.
Key metrics serve as critical indicators that guide decision-making processes in SAS business intelligence (BI) projects. These metrics enable organizations to assess performance, identify trends, and formulate strategies based on data-driven insights. By focusing on the right key metrics, businesses can enhance operational efficiency, drive growth, and achieve competitive advantages.The role of key metrics in SAS projects extends beyond mere data collection; they are essential for translating raw data into meaningful insights.
Various metrics can significantly influence project outcomes, guiding stakeholders in making informed decisions. For instance, metrics such as customer acquisition cost, return on investment, and churn rate provide valuable insights that impact budget allocation, marketing strategies, and customer retention efforts.
Impact of Different Metrics on Project Outcomes
Understanding the impact of different metrics is crucial for the success of SAS business intelligence projects. Each metric can provide unique insights into specific operational aspects, ultimately affecting overall project performance. The following metrics are pivotal in shaping project outcomes:
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): This metric measures the total cost of acquiring a new customer. A lower CAC indicates efficient marketing strategies and successful sales processes, directly impacting profitability.
- Return on Investment (ROI): ROI helps businesses gauge the profitability of their investments in SAS BI projects. A higher ROI reflects effective resource utilization and contributes to strategic planning.
- Churn Rate: This metric represents the percentage of customers who stop using a service within a given time frame. Lowering churn rates can lead to increased customer loyalty and sustained revenue growth.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): NPS measures customer satisfaction and loyalty by asking customers how likely they are to recommend a service. This feedback is invaluable for refining customer experience and service offerings.
- Data Accuracy and Quality Metrics: These metrics assess the reliability and validity of data used in SAS projects. High data quality ensures better decision-making and enhances the credibility of insights derived from the BI system.
Several businesses have effectively utilized key metrics in their SAS BI projects, achieving notable results. For example, a retail company that tracked its customer acquisition cost saw a significant reduction in expenses by refining its marketing strategies based on analyzed data. Similarly, a financial institution that monitored its churn rate implemented targeted retention campaigns, leading to a decrease in customer attrition and an increase in overall revenue.
These examples illustrate the powerful impact that key metrics can have on business outcomes when integrated into SAS BI projects.
Types of Key Metrics to Track
In the realm of SAS business intelligence projects, understanding the types of key metrics to track is crucial for effective decision-making. The right metrics provide insights into various aspects of business performance, enabling organizations to optimize operations, enhance productivity, and drive financial growth.Metrics can broadly be categorized into three main types: performance, operational, and financial metrics. Each of these categories serves a distinct purpose and helps organizations gauge different facets of their activities.
Performance metrics focus on the efficiency and effectiveness of strategies; operational metrics offer insights into day-to-day activities; financial metrics assess the monetary aspects of the business, ensuring sustainability and profitability.
Performance, Operational, and Financial Metrics
To comprehensively understand the various types of metrics essential for SAS business intelligence projects, it is important to delve into each category. Performance metrics typically include indicators such as return on investment (ROI) and customer satisfaction scores, which help organizations evaluate the success of strategic initiatives. Operational metrics, on the other hand, encompass measures like cycle time and throughput, providing insights into the efficiency of processes.
Lastly, financial metrics, including profit margins and revenue growth rates, shed light on the financial health of the organization.Additionally, metrics can be divided into quantitative and qualitative dimensions. Quantitative metrics are numerical and can be easily measured and analyzed, such as sales figures or website traffic. Conversely, qualitative metrics are descriptive and often subjective, such as customer feedback or employee satisfaction levels.The following table categorizes specific metrics by type and provides their definitions:
| Metric Type | Specific Metric | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Performance | Return on Investment (ROI) | A measure of the profitability of an investment, calculated as the net profit divided by the cost of the investment. |
| Performance | Customer Satisfaction Score | A metric that measures how products or services supplied by a company meet or surpass customer expectation. |
| Operational | Cycle Time | The total time from the beginning to the end of a process, reflecting efficiency in operations. |
| Operational | Throughput | The amount of work or number of units produced in a given time period, indicating productivity levels. |
| Financial | Profit Margin | A financial metric that shows the percentage of revenue that exceeds the costs of production. |
| Financial | Revenue Growth Rate | The rate at which a company’s revenue increases over a specific period, reflecting business health and expansion. |
“Tracking the right key metrics in SAS business intelligence is pivotal for informed decision-making and strategic planning.”
Tools and Techniques for Measuring Key Metrics
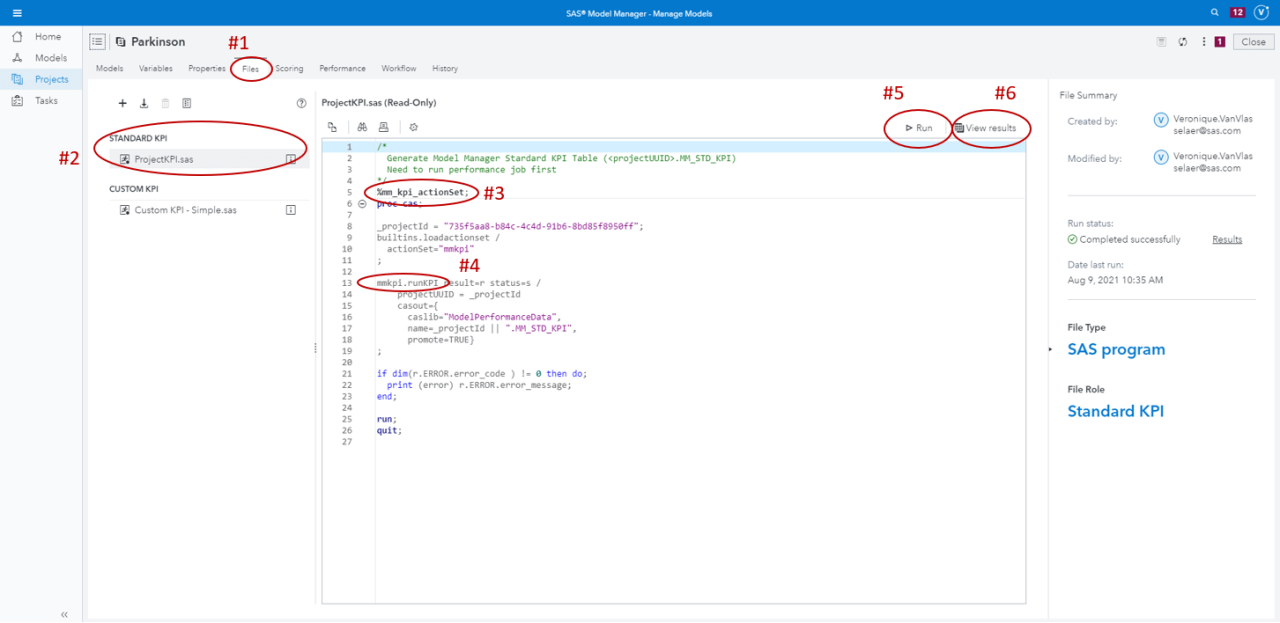
In business intelligence projects, particularly those utilizing SAS, leveraging the right tools and techniques is crucial for effectively measuring key metrics. These tools enable organizations to collect, analyze, and visualize data that informs decision-making and strategy. Understanding how to utilize these resources is essential for maximizing the performance and impact of business intelligence initiatives.
Methods for Collecting and Analyzing Key Metrics
Employing a systematic approach to collect and analyze key metrics is fundamental in any SAS business intelligence project. The following methods are recognized for their effectiveness in facilitating accurate data collection and analysis:
- SAS Data Integration Studio: This tool allows users to connect various data sources, transforming raw data into actionable insights. It helps automate data extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL) processes.
- SAS Enterprise Guide: A user-friendly interface that allows analysts to perform sophisticated data analysis without requiring deep programming knowledge. It enhances the ability to create reports and visualizations directly linked to the data.
- SAS Visual Analytics: This tool provides powerful visualization capabilities, enabling users to create interactive dashboards and reports that make key metrics easily understandable and accessible.
- SAS Viya: An advanced analytics platform that supports machine learning and data mining, offering capabilities for real-time data processing and analytics.
Best Practices for Using SAS Tools to Visualize and Report on Key Metrics
Visualization and reporting play critical roles in communicating key metrics effectively. The following best practices should be observed to enhance clarity and engagement:
- Utilize Dashboards: Create dashboards that aggregate key metrics in a single view. This allows stakeholders to quickly assess performance and identify trends.
- Implement Clear Visualizations: Choose the right type of chart or graph to represent data accurately. For example, bar graphs for comparisons and line charts for trends over time.
- Maintain Consistency: Ensure uniformity in visualizations across reports to help users recognize patterns and interpret data quickly.
- Incorporate Interactive Elements: Use interactive features that allow users to drill down into specific metrics, enhancing understanding and decision-making capabilities.
Significance of Data Quality on Metric Accuracy
The accuracy of key metrics is heavily influenced by the quality of the underlying data. High-quality data is essential for reliable analysis and reporting. Consider the following points regarding data quality:
- Data Validation: Implement robust validation mechanisms to ensure the accuracy of collected data. This includes checks for duplicates, errors, and inconsistencies.
- Regular Audits: Conduct periodic audits of data to identify and rectify any quality issues. This helps maintain the integrity of key metrics over time.
- Standardization: Establish data entry standards to minimize variations and errors. Consistent formats and definitions enhance data reliability.
- Training: Provide training for personnel involved in data collection and management processes to ensure adherence to quality protocols.
Challenges in Tracking Key Metrics
Tracking key metrics in SAS business intelligence projects presents various challenges that organizations must navigate to ensure informed decision-making and effective performance measurement. Understanding these challenges is crucial for optimizing the tracking process and enhancing overall project effectiveness.Organizations often face issues related to data quality, integration, and user engagement when attempting to track key metrics. The complexity of data sources and the rapid pace of change in business environments can complicate the tracking process, leading to inaccurate or incomplete data.
Additionally, the lack of a clear definition of what constitutes a key metric can further hinder the tracking efforts.
Common Challenges in Metric Tracking
The following Artikels the challenges organizations typically encounter while tracking key metrics in SAS BI projects:
- Data Quality Issues: Inconsistent, inaccurate, or outdated data can lead to misleading conclusions. Data integrity is essential for reliable metric tracking.
- Integration Difficulties: Combining data from various sources can be complex, resulting in fragmented insights and a lack of comprehensive context.
- User Adoption Challenges: Low engagement from users can stem from a lack of understanding of the metrics’ importance, leading to underutilization of BI tools.
- Dynamic Business Environment: Rapid changes in business conditions can render previously defined key metrics less relevant, necessitating continual reevaluation.
- Resource Constraints: Limited personnel or budget can restrict the ability to accurately track and analyze metrics.
To address these challenges effectively, organizations can implement several strategies that enhance the tracking processes. By fostering a robust infrastructure and promoting a culture of data-driven decision-making, organizations can significantly improve their ability to track key metrics.
Strategies for Overcoming Tracking Challenges, Key metrics to track in SAS business intelligence projects.
The following solutions serve to mitigate the challenges associated with tracking key metrics:
- Enhancing Data Governance: Implement stringent data governance policies to ensure data accuracy, consistency, and security.
- Streamlining Data Integration: Utilize advanced integration tools and techniques to ensure seamless data flow from multiple sources.
- Improving User Training: Conduct comprehensive training sessions to help users understand the relevance and application of key metrics.
- Regular Metric Review: Establish a routine for reviewing and updating key metrics to align with changing business needs.
- Allocating Resources Wisely: Ensure adequate resources and personnel are dedicated to the task of metric tracking and analysis.
Implementing these strategies effectively can lead to a more streamlined and accurate tracking process, ultimately enhancing the value derived from SAS business intelligence projects.