Exploring the future trends of SAS business intelligence technology. presents a compelling narrative that delves into the transformative impact of emerging technologies on the SAS landscape. As organizations increasingly leverage machine learning and artificial intelligence, the capabilities of SAS business intelligence are being reshaped to meet the demands of a data-driven world. Furthermore, the integration of cloud computing is revolutionizing how data is stored, accessed, and analyzed, enhancing the overall accessibility and scalability of SAS tools.
This discussion also highlights the innovative advancements in data visualization and reporting, ensuring that stakeholders can derive actionable insights efficiently.
The significance of data governance is paramount as well, laying the groundwork for effective data management practices. Establishing robust frameworks is essential for maintaining data quality and security, particularly in an era marked by stringent regulatory compliance challenges. Additionally, user experience continues to evolve, with modern interfaces designed to improve engagement and satisfaction among SAS users. By examining the adoption trends across various sectors, we gain a deeper understanding of how organizations are embracing SAS business intelligence tools.
Emerging Technologies in SAS Business Intelligence
The landscape of SAS Business Intelligence (BI) is rapidly evolving, driven by the advent of emerging technologies that enhance data analytics and decision-making processes. Machine learning, artificial intelligence (AI), and cloud computing are pivotal in transforming how organizations utilize SAS technologies. These advancements not only streamline operations but also improve the accuracy and relevance of insights derived from vast datasets.
Machine Learning and AI in SAS Business Intelligence
Machine learning and AI are revolutionizing the capabilities of SAS Business Intelligence by enabling advanced analytics and predictive modeling. These technologies facilitate the extraction of meaningful patterns from complex data, leading to more informed decision-making. For instance, SAS’s integration of AI capabilities allows for automated data preparation, which reduces the time analysts spend on data wrangling. This is critical for organizations that need to rapidly adapt to market changes.
Furthermore, machine learning algorithms enhance forecasting abilities by analyzing historical data to identify trends and predict future outcomes.
“AI enhances SAS BI by enabling sophisticated algorithms to provide predictive insights, thereby driving strategic business initiatives.”
Integration of Cloud Computing with SAS Technologies
The incorporation of cloud computing into SAS technologies has significantly altered the BI landscape by providing scalable and flexible solutions for data storage and processing. This integration allows organizations to leverage the power of cloud infrastructure to handle large datasets efficiently, facilitating real-time analytics and collaboration.Organizations utilizing SAS on cloud platforms can experience lower operational costs, improved accessibility, and enhanced collaboration among teams.
The cloud environment supports various SAS tools, enabling users to deploy analytical models and generate insights without the constraints of traditional on-premises systems.
“Cloud computing enables SAS users to scale their BI capabilities, ensuring they remain agile and responsive to business needs.”
Innovations in Data Visualization and Reporting Tools
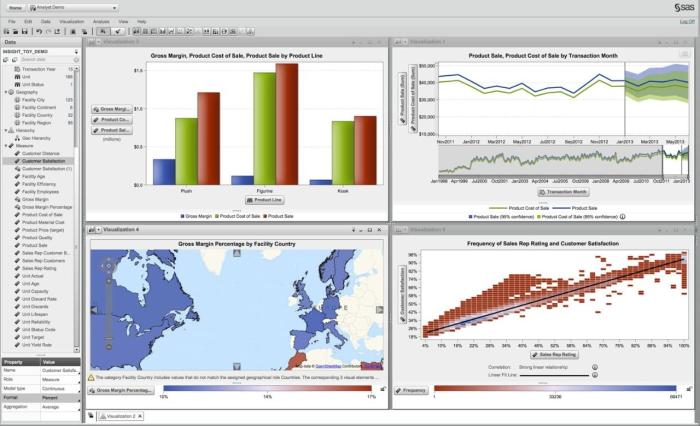
Innovations in data visualization and reporting tools within SAS are critical for transforming raw data into actionable insights. Enhanced visualization capabilities allow users to create more intuitive and interactive dashboards that facilitate data exploration.Recent advancements have introduced features such as augmented analytics, which utilizes AI to assist in data interpretation, automatically generating insights and recommendations. Additionally, SAS has developed advanced reporting tools that support various data visualization formats including graphs, charts, and heat maps, which make it easier for stakeholders to understand complex data sets.These tools empower users to present information in a way that resonates with different audiences, ensuring clarity and promoting informed decision-making across all organizational levels.
“Effective data visualization is essential for communicating insights, making complex data accessible to all stakeholders.”
The Role of Data Governance in Future SAS BI
Data governance plays a critical role in shaping the future of SAS Business Intelligence (BI) by ensuring that data is reliable, secure, and compliant with regulations. In an era where data is increasingly recognized as a corporate asset, robust governance frameworks are essential for SAS users to leverage data effectively while mitigating risks associated with data misuse and non-compliance.A comprehensive data governance framework is vital for maintaining high data quality and security standards within SAS environments.
It encompasses policies, processes, and technologies that facilitate the management of data integrity, availability, and confidentiality. Effective governance ensures that users can trust the insights derived from SAS BI tools, which are crucial for informed decision-making.
Importance of Data Governance Frameworks for SAS Users
Implementing a strong data governance framework is essential for SAS users for several reasons. These frameworks help establish clear accountability for data management, ensuring that data stewards are responsible for maintaining data quality and security. Key components of a robust data governance framework include:
- Data Ownership: Assigning clear ownership allows for better accountability and stewardship over data assets.
- Data Policies and Standards: Establishing policies ensures that data is handled consistently and in compliance with industry standards.
- Data Stewardship: Designating data stewards to oversee specific datasets enhances data quality and facilitates resolution of data-related issues.
- Monitoring and Auditing: Regular assessments of data quality and compliance help identify and mitigate risks in real-time.
Best Practices for Ensuring Data Quality and Security in SAS Environments
Ensuring data quality and security within SAS environments is paramount, particularly as organizations increasingly rely on data-driven strategies. The following best practices can enhance data governance efforts in SAS BI:
1. Implement Data Quality Frameworks
Develop frameworks that assess data accuracy, completeness, and consistency regularly.
2. Utilize Metadata Management
Maintain a detailed inventory of metadata to enhance data understanding and governance practices.
3. Conduct Regular Training Programs
Equip users with knowledge about data governance policies and practices to foster a culture of compliance.
4. Integrate Security Protocols
Implement role-based access controls (RBAC) to regulate who can view or manipulate data within SAS environments.
5. Leverage Automated Data Profiling Tools
Employ SAS tools that offer automated data profiling to identify anomalies and inconsistencies.
Regulatory Compliance Challenges for SAS Business Intelligence
In a landscape marked by evolving regulations, SAS users face significant compliance challenges that necessitate a proactive approach to data governance. Adhering to regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA is essential for organizations that handle sensitive data.Challenges include:
- Data Privacy Concerns: Ensuring that personal data is handled according to regulatory requirements is challenging and requires meticulous oversight.
- Cross-Border Data Transfers: Navigating the complexities of international data transfers can complicate compliance efforts.
- Audit Readiness: Organizations must maintain comprehensive documentation and reporting capabilities to demonstrate compliance during audits.
- Rapidly Changing Regulations: Keeping up with evolving data protection laws requires ongoing training and adaptation of governance frameworks.
User Experience and Adoption Trends: Exploring The Future Trends Of SAS Business Intelligence Technology.
The landscape of user experience in SAS business intelligence (BI) technology has undergone significant transformation in recent years. As organizations increasingly rely on data-driven decision-making, enhancing the user interface (UI) design and ensuring high user engagement have become critical factors for successful adoption of SAS BI tools. This segment delves into the evolving UI designs, strategies for bolstering user satisfaction, and an analysis of adoption rates across various industries.
Evolving User Interface Designs, Exploring the future trends of SAS business intelligence technology.
The user interface of SAS business intelligence platforms has transformed to prioritize user-friendliness and accessibility. Modern UI design trends emphasize intuitive navigation, visual clarity, and interactive elements that cater to both novice and advanced users. The integration of responsive design ensures that users can effectively access BI tools across various devices, including smartphones and tablets. Key design features enhancing the user experience include:
- Dashboard Customization: Users can tailor dashboards to meet their specific needs, allowing for a more personalized and relevant experience.
- Data Visualization Tools: Enhanced graphics and visualization capabilities help users interpret complex data sets through charts, graphs, and maps.
- Natural Language Processing: This feature enables users to interact with the BI tools using everyday language, simplifying data queries without needing technical expertise.
- Collaboration Features: Built-in tools for sharing insights and collaborating with team members promote a unified approach to data analysis.
Strategies for Enhancing User Engagement and Satisfaction
To maximize user engagement and satisfaction with SAS BI tools, organizations can implement several effective strategies. By focusing on training, support, and feedback mechanisms, companies can foster a culture of data literacy and encourage the effective use of BI tools.Implementing the following strategies is crucial for improving user engagement:
- Comprehensive Training Programs: Offering regular training sessions helps users become proficient with the tools, enhancing their confidence in utilizing the features available.
- User-Centric Documentation: Providing easily accessible resources, such as user guides and tutorial videos, ensures users can find the information they need quickly.
- Feedback Loops: Establishing channels for user feedback allows organizations to address concerns and continuously improve the user experience based on actual user input.
- Gamification Elements: Incorporating elements of gamification, such as rewards for achieving milestones within the BI tools, can encourage consistent usage and exploration of features.
Adoption Rates Across Industries and Sectors
The adoption rates of SAS BI tools vary significantly across different industries, influenced by factors such as data maturity, organizational culture, and specific business needs. Industries such as finance, healthcare, and retail have shown particularly high adoption rates due to their reliance on analytics for operational efficiency and strategic decision-making.Key insights into adoption trends include:
- Finance: The finance sector has embraced SAS BI tools to enhance reporting accuracy and risk management, often boasting adoption rates exceeding 75% among major firms.
- Healthcare: With a growing emphasis on data-driven patient care, healthcare organizations have increasingly adopted SAS BI tools to streamline operations and improve patient outcomes.
- Retail: Retail companies utilize SAS BI to analyze consumer behavior and optimize inventory management, resulting in significant adoption, especially among large retailers.
- Manufacturing: In this sector, the adoption of SAS BI tools is rising, driven by the need for real-time data analytics to enhance operational performance.
The Impact of Real-Time Analytics
Real-time analytics has emerged as a pivotal component in the SAS business intelligence landscape, allowing organizations to process and analyze data instantaneously. This capability not only enhances decision-making processes but also empowers businesses to respond swiftly to market changes and customer demands. The significance of real-time data processing lies in its ability to transform raw data into actionable insights in a fraction of the time it would traditionally take.Implementing real-time analytics within SAS environments requires a structured approach that integrates data sources, processing technologies, and analytical tools.
A well-defined framework helps organizations leverage real-time data effectively.
Framework for Implementing Real-Time Analytics
Establishing a comprehensive framework for real-time analytics involves several key components. Below are the essential elements that organizations should consider:
- Data Integration: Seamless integration of diverse data sources, including streaming data from IoT devices, social media platforms, and transaction systems, is crucial. This ensures that all relevant data is available for analysis in real-time.
- Processing Technologies: Utilizing technologies such as Apache Kafka for data streaming and SAS Event Stream Processing for real-time analytics enables organizations to handle large volumes of data with low latency.
- Analytical Tools: Incorporating SAS Visual Analytics for interactive reporting and visualization aids in quickly interpreting real-time insights, facilitating faster decision-making.
- Data Governance: Implementing data governance policies ensures the accuracy, security, and compliance of real-time analytics efforts, establishing trust in the insights produced.
- Training and Culture: Fostering a culture that embraces data-driven decision-making and investing in employee training on real-time analytics tools empowers teams to utilize these technologies effectively.
The benefits of real-time analytics are substantial, contributing significantly to enhanced organizational efficiency and responsiveness. However, organizations must also navigate certain challenges that accompany this approach.
Benefits and Challenges of Real-Time Decision-Making
Real-time analytics presents numerous advantages, particularly in enhancing agility and operational performance. Organizations that adopt this technology can experience:
- Improved Customer Engagement: Immediate insights into customer behavior allow businesses to tailor their offerings and communication strategies in real-time, enhancing the overall customer experience.
- Proactive Decision-Making: By analyzing real-time data, organizations can identify emerging trends and potential issues before they escalate, enabling proactive strategies rather than reactive measures.
- Increased Efficiency: Streamlining operations through real-time data analysis helps eliminate bottlenecks and optimize workflows, ultimately leading to cost savings.
Despite these benefits, organizations face challenges when implementing real-time decision-making:
- Data Overload: The sheer volume of data generated in real-time can overwhelm systems and lead to information paralysis if not managed correctly.
- Integration Complexities: Integrating legacy systems with modern real-time analytics platforms can pose significant technical challenges and require substantial resources.
- Skill Gaps: Ensuring that staff possesses the necessary skills to interpret and act on real-time data insights can be a barrier to successful implementation.
In conclusion, while real-time analytics represents a transformative force in SAS business intelligence, organizations must carefully construct their framework and address inherent challenges to fully harness its potential.