Comparing SAS business intelligence with other BI tools. sets the stage for an insightful exploration into the dynamic realm of business intelligence. As organizations increasingly rely on data to drive decision-making, understanding the unique advantages and capabilities of SAS Business Intelligence becomes imperative. This examination not only highlights the strengths of SAS BI but also positions it against notable competitors, providing a comprehensive view that aids businesses in selecting the right tools for their strategic needs.
SAS Business Intelligence is renowned for its robust features, including advanced data visualization and reporting capabilities, which cater to various industries seeking to leverage data for enhanced insights. In this exploration, we will delve into the specific functionalities that make SAS BI a preferred choice, particularly in sectors such as finance, healthcare, and retail, where data-driven decisions are critical.
Overview of SAS Business Intelligence
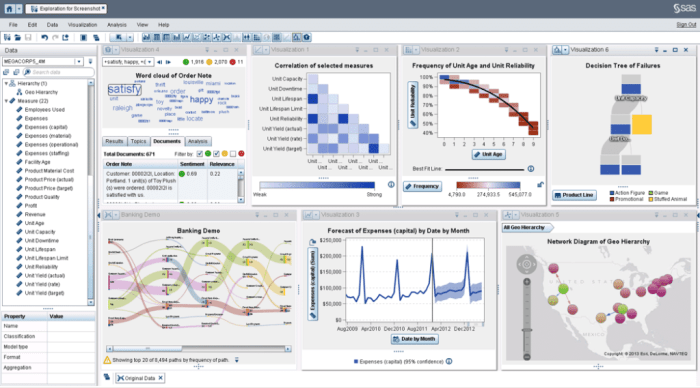
SAS Business Intelligence (BI) is a robust suite of tools designed to facilitate data analysis, visualization, and reporting. Leveraging advanced analytics, SAS BI empowers organizations to make data-driven decisions by transforming raw data into meaningful insights. The platform’s capabilities extend across various dimensions of business intelligence, providing comprehensive solutions for both technical and non-technical users.SAS Business Intelligence encompasses a wide range of features and functionalities that enhance data visualization and reporting.
Key components include intuitive dashboards, advanced analytics, and self-service reporting. Users can easily create interactive reports and visualizations that enable them to explore data patterns and trends effectively. The platform supports collaboration among teams, allowing users to share insights and dashboards seamlessly.
Main Features and Functionalities
The primary features of SAS Business Intelligence contribute significantly to its popularity across various sectors. These features include:
- Data Integration: SAS BI offers powerful data integration capabilities, allowing users to capture and consolidate data from diverse sources such as databases, spreadsheets, and cloud applications.
- Advanced Analytics: The platform includes analytical tools that support predictive modeling, statistical analysis, and machine learning, enabling organizations to derive deeper insights from their data.
- Customizable Dashboards: Users can create personalized dashboards that showcase key performance indicators (KPIs) and other critical metrics tailored to their specific business needs.
- Self-Service Reporting: SAS BI empowers users to generate reports independently, reducing reliance on IT and enhancing agility in decision-making processes.
- Collaboration Tools: The platform encourages teamwork by allowing users to share reports and dashboards, facilitating a collaborative approach to data-driven decision-making.
Advantages in Data Visualization and Reporting, Comparing SAS business intelligence with other BI tools.
SAS Business Intelligence excels in data visualization and reporting, offering several advantages that enhance user experience and decision-making:
- Intuitive User Interface: The user-friendly interface simplifies the creation of visualizations, making it accessible for users with varying levels of technical expertise.
- Dynamic Visualizations: SAS BI provides interactive visualizations that allow users to drill down into data, uncovering insights that static reports may not reveal.
- Real-Time Reporting: The platform supports real-time data updates, ensuring that users have access to the most current information for timely decision-making.
- Comprehensive Reporting Options: Users can generate a variety of report formats, including PDFs, Excel sheets, and web-based reports, catering to different stakeholder needs.
Industries Using SAS Business Intelligence
SAS Business Intelligence is prominently utilized across various industries, each benefiting from its unique capabilities. Notable sectors include:
- Healthcare: In healthcare, SAS BI is used for patient data analysis, resource allocation, and performance measurement to enhance patient outcomes.
- Financial Services: Financial institutions leverage SAS BI for risk management, fraud detection, and compliance reporting, helping maintain regulatory standards.
- Retail: Retailers utilize SAS BI to analyze customer behavior, optimize inventory management, and improve sales forecasting efforts.
- Manufacturing: SAS BI aids manufacturers in supply chain management, quality control, and production efficiency analysis.
- Education: Educational institutions adopt SAS BI to assess student performance, streamline administrative processes, and enhance learning outcomes.
Comparison with Other Business Intelligence Tools
SAS Business Intelligence (BI) is a powerful tool for data analysis and reporting, but it is essential to analyze how it compares to other prominent BI tools in the market. Understanding the differences can help organizations choose the right solution based on their specific needs and objectives.
Comparison of SAS Business Intelligence and Tableau
Tableau is known for its data visualization capabilities and intuitive interface. In contrast, SAS Business Intelligence offers a more comprehensive suite that includes advanced analytics and data management features. Some key differences include:
- Visualization vs. Analytics: Tableau excels in creating visually appealing graphs and dashboards, while SAS provides more robust analytical tools for deep statistical analysis.
- User Interface: Tableau’s drag-and-drop functionality makes it user-friendly for those without technical expertise, whereas SAS may have a steeper learning curve due to its extensive functionality.
- Data Preparation: SAS BI includes powerful data preparation capabilities, allowing users to clean and manipulate data before analysis, which is less emphasized in Tableau.
- Integration and Deployment: SAS BI can integrate with a wide range of data sources and systems, often requiring more configuration, whereas Tableau offers seamless integration with many popular databases and cloud services.
Comparison of SAS Business Intelligence and Microsoft Power BI
Microsoft Power BI is recognized for its affordability and ease of use, especially for organizations already utilizing Microsoft products. In comparing it with SAS BI, the following points stand out:
- Ease of Use: Power BI is designed for users to quickly create dashboards and reports with minimal training, while SAS BI can require a more extensive understanding of analytics and data management.
- Integration: Although SAS BI integrates well with various data sources, Power BI offers seamless integration with Microsoft Excel and Azure, making it a preferred choice for organizations heavily invested in the Microsoft ecosystem.
- Cost: Power BI is generally more cost-effective for small to medium-sized businesses, whereas SAS BI may come with a higher licensing fee, reflecting its extensive capabilities.
Comparison of SAS Business Intelligence and QlikView
QlikView is celebrated for its associative data model and powerful self-service capabilities. When comparing SAS Business Intelligence with QlikView, several important distinctions emerge:
- Data Analysis Capabilities: SAS BI is renowned for its advanced statistical analysis and predictive modeling features, which may surpass those offered by QlikView.
- Associative vs. Relational: QlikView operates on an associative model, allowing users to explore data freely without predefined queries. In contrast, SAS BI relies on a more structured approach, which may be beneficial for in-depth analysis.
- User Experience: While QlikView offers a highly interactive and user-driven experience, SAS BI provides comprehensive reporting and visualization tools but may not be as intuitive for casual users.
Use Cases and Applications
SAS Business Intelligence (BI) has demonstrated its capabilities across various sectors, enabling organizations to leverage data for informed decision-making. The following sections explore successful implementations of SAS BI, illustrating its effectiveness in real-world scenarios. Specific examples highlight how SAS BI can outperform other BI tools, particularly in areas requiring complex analytics and data integration.
Successful Implementations of SAS Business Intelligence
Numerous organizations have successfully implemented SAS Business Intelligence to enhance their data-driven decision-making processes. For instance, a major healthcare provider utilized SAS BI to streamline patient care analytics, integrating clinical data with operational metrics. This approach led to improved patient outcomes, as real-time insights allowed healthcare professionals to make timely decisions.Another notable case involved a financial institution that adopted SAS BI to combat fraud.
By leveraging advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms, the bank could identify suspicious transactions in real time, significantly reducing losses from fraudulent activities. Such implementations underscore the versatility and power of SAS BI in various industries.
Scenarios Where SAS BI Outperforms Competitors
In scenarios requiring complex data processing and advanced analytical capabilities, SAS BI consistently shows superior performance. The following examples illustrate SAS BI’s strengths compared to other BI tools:
- A retail chain faced challenges in inventory management due to inaccurate forecasting. By employing SAS BI, the company implemented predictive analytics that improved inventory turnover rates by 20% compared to previous methods. In contrast, other BI tools provided basic reporting features that failed to address the intricacies of demand forecasting.
- In the telecommunications sector, a leading provider used SAS BI to enhance customer experience through churn analysis. Utilizing SAS’s advanced data mining capabilities, the company could identify at-risk customers and implement targeted retention strategies, resulting in a 15% decrease in churn rates. Competing tools could not match the depth of analysis required for such nuanced insights.
The following table summarizes various use cases for SAS BI versus its competitors, illustrating strengths in distinct scenarios:
| Use Case | SAS BI | Competitors |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare Analytics | Integrates clinical and operational data for real-time insights | Basic reporting tools with limited integration capabilities |
| Fraud Detection | Utilizes machine learning for real-time fraud detection | Static analysis with slower response times |
| Inventory Management | Predictive analytics leading to improved turnover | Simple dashboards that lack forecasting accuracy |
| Customer Retention | Advanced data mining to identify and target at-risk customers | Basic analytics that miss nuanced customer behaviors |
These examples and comparisons illustrate SAS Business Intelligence’s significant advantages in providing comprehensive analytics, enabling organizations to make informed decisions that drive success.
Future Trends in Business Intelligence: Comparing SAS Business Intelligence With Other BI Tools.
The landscape of Business Intelligence (BI) is continually evolving, driven by advancements in technology and changing market demands. As organizations seek more effective solutions for data analysis and decision-making, SAS Business Intelligence and its competitors must adapt to these emerging trends. This section delves into the future trends that may shape BI tools, particularly SAS, and explores the potential advancements in technology that could influence its market standing.
Impact of Advanced Analytics and Predictive Modeling
Advanced analytics and predictive modeling are becoming increasingly vital in the BI realm. These techniques allow organizations to forecast trends, identify patterns, and enhance data-driven decision-making. SAS Business Intelligence is well-positioned to harness these advancements due to its robust analytical capabilities.The integration of predictive analytics into SAS can lead to improved outcomes across various sectors. For example, in healthcare, predictive modeling can anticipate patient needs, thus optimizing resource allocation.
Additionally, retail businesses can develop targeted marketing strategies based on consumer behavior predictions.
Artificial Intelligence Integration in Business Intelligence
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) is set to redefine the capabilities of Business Intelligence tools, including SAS. AI enhances BI by automating data preparation and enabling more sophisticated data analysis, which can significantly reduce the time required for reporting and insights generation. Key implications of AI on SAS Business Intelligence include:
- Enhanced Data Processing: AI algorithms can process vast amounts of data quickly and identify trends that may not be immediately visible to human analysts.
- Natural Language Processing: AI can facilitate user interactions with BI tools through natural language queries, allowing non-technical users to extract insights without needing deep analytical skills.
- Real-time Analytics: AI-powered BI tools can provide real-time insights, enabling businesses to make timely decisions based on the latest data.
Moreover, the ability to incorporate machine learning models into SAS can provide organizations with predictive insights that adapt over time, fundamentally changing how decisions are made.
Cloud Computing and Scalability
The shift towards cloud computing continues to impact the BI landscape, including SAS Business Intelligence. Cloud solutions offer scalability, cost-effectiveness, and enhanced collaboration, allowing users to access data from anywhere at any time.The advantages of cloud computing in the context of SAS include:
- Scalable Resources: Organizations can scale their BI solutions according to demand, ensuring optimal performance without the need for significant upfront investment in infrastructure.
- Collaboration Opportunities: Cloud-based BI tools facilitate easier sharing of insights across teams and departments, fostering a culture of data-driven decision-making.
- Frequent Updates: Cloud solutions often receive regular updates, ensuring users benefit from the latest features and security enhancements.
As organizations increasingly embrace cloud technology, SAS Business Intelligence must evolve to maintain its competitive edge in this new environment.
Data Governance and Security Considerations
As data privacy regulations and corporate governance become more stringent, the importance of robust data governance and security measures in BI tools cannot be overstated. SAS Business Intelligence will need to adapt its offerings to ensure compliance with regulations such as GDPR and CCPA.Strategic focus areas for SAS to enhance data governance include:
- Enhanced Data Security: Implementing advanced security protocols to protect sensitive information and ensure that data is accessed only by authorized users.
- Data Lineage Tracking: Providing tools to track the origin and transformation of data, ensuring transparency and accountability in data usage.
- Automated Compliance Reporting: Developing features that assist organizations in generating compliance reports, reducing administrative burdens while maintaining adherence to regulations.
As businesses navigate tighter regulations, SAS’s capabilities in data governance will be critical in maintaining trust and reliability in its BI solutions.