Benefits of using SAS for business intelligence analytics. are manifold, offering organizations a powerful tool to enhance their data-driven decision-making processes. SAS stands out in the competitive landscape of analytics solutions by seamlessly integrating with various data sources, thereby enriching the analytical capabilities of businesses. Furthermore, the emphasis on data visualization within SAS not only aids in interpreting complex datasets but also significantly influences strategic planning and execution.
With its robust features, SAS enables businesses to convert raw data into actionable insights, fostering an environment where informed decisions can thrive. Its adaptability ensures that organizations of all sizes can leverage its capabilities, making it an invaluable asset in today’s data-centric world.
Overview of SAS in Business Intelligence
SAS (Statistical Analysis System) plays a pivotal role in enhancing business intelligence capabilities by providing organizations with powerful tools for data analysis, reporting, and visualization. Its comprehensive suite of software solutions allows businesses to harness their data effectively, enabling informed decision-making and strategic planning. By integrating analytical methods with data management, SAS empowers companies to transform raw data into actionable insights.SAS seamlessly integrates with various data sources, including databases, spreadsheets, and cloud services, ensuring that users can access, manage, and analyze data from multiple platforms.
This capability is vital for organizations that rely on diverse data streams for their analytics. SAS supports numerous data formats and offers robust data connectivity, allowing users to extract insights without facing barriers related to data silos. As a result, organizations can achieve a unified view of their data landscape, leading to more accurate analysis and improved operational efficiency.
Importance of Data Visualization in SAS
Effective data visualization is crucial for translating complex data into understandable insights, significantly impacting decision-making processes. SAS excels in providing advanced visualization tools that allow users to create compelling graphical representations of their data. These visualizations facilitate a clearer comprehension of trends, patterns, and anomalies, which might otherwise be obscured in raw datasets.The integration of visualization techniques in SAS promotes better communication of insights among stakeholders.
Key features of SAS visualization include interactive dashboards, customizable reports, and a variety of chart and graph types, each designed to present data in the most impactful way. The following points emphasize the significance of data visualization in SAS:
-
Enhances Data Interpretation: Visualization simplifies complex data, making it easier to identify key trends and outliers.
-
Facilitates Quick Decision-Making: Interactive visualizations allow decision-makers to explore data dynamically, leading to faster insights.
-
Improves Stakeholder Engagement: Engaging visuals enhance presentations, capturing attention and facilitating discussions among team members.
-
Enables Predictive Analytics: Visual tools help in illustrating predictive models, making it easier to convey potential future outcomes based on historical data.
SAS’s commitment to visualization not only aids in presenting data effectively but also plays a crucial role in fostering a data-driven culture within organizations, promoting informed decisions at all levels of management. This synergy between analytics and visualization is essential for businesses striving to maintain a competitive edge in today’s data-centric landscape.
Key Benefits of Using SAS for Analytics
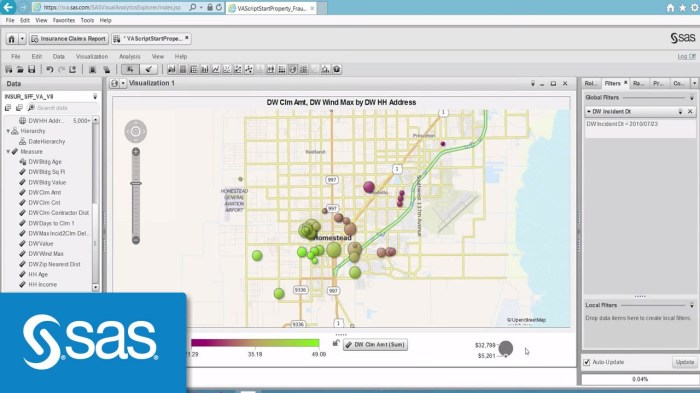
The decision to adopt a robust analytics tool can significantly influence a business’s operational efficiency and strategic decision-making capabilities. SAS (Statistical Analysis System) stands out as a preferred choice among organizations due to its powerful analytics capabilities, flexibility, and comprehensive support for business intelligence. Understanding the key benefits of using SAS for analytics can help businesses maximize their data-driven insights.One of the primary advantages of SAS lies in its ability to provide a wide array of advanced analytics functions, enabling users to perform complex data analysis with ease.
SAS distinguishes itself from other analytics tools through its strong focus on data governance, security features, and comprehensive support for various data formats. This combination of features allows businesses to ensure data integrity while leveraging insights for strategic initiatives.
Scalability of SAS for Businesses of Different Sizes, Benefits of using SAS for business intelligence analytics.
SAS is designed to accommodate the varying needs of businesses, regardless of their size or industry. Its scalable architecture allows organizations to start small and grow their analytics capabilities as their data needs evolve. This scalability is critical in today’s fast-paced business environment, where the volume and complexity of data are constantly increasing.
- Enterprises can benefit from SAS’s ability to handle large datasets seamlessly, ensuring that performance remains optimal even as data volume grows.
- Middle-market companies can leverage SAS’s modular approach, allowing them to adopt specific functionalities tailored to their current requirements while maintaining the flexibility to expand in the future.
- Small businesses can utilize SAS’s user-friendly interface and simplified analytics tools, enabling them to harness the power of data without extensive technical expertise.
SAS has been successfully implemented in various organizations, demonstrating its impact on business performance. For instance, a retail chain utilized SAS to analyze customer buying patterns, resulting in a 15% increase in sales through targeted marketing campaigns. Similarly, a healthcare provider adopted SAS to enhance patient care and optimize resource allocation, leading to a 20% reduction in operational costs. Such case studies exemplify how SAS can transform data into actionable insights, driving significant improvements in overall performance.
“SAS provides a comprehensive and flexible analytics environment, enabling businesses to derive meaningful insights from their data.”
The ability to scale, adapt, and provide actionable insights makes SAS an invaluable tool for businesses looking to improve their analytics capabilities and drive performance.
Features and Functionalities of SAS
SAS (Statistical Analysis System) is renowned for its extensive features and functionalities tailored for business intelligence analytics. Its robust capabilities enable businesses to leverage data effectively, make informed decisions, and gain a competitive edge. Understanding the major features of SAS not only highlights its unique offerings but also elucidates how it stands out in the crowded analytics landscape.SAS includes a comprehensive suite of tools that cater to various aspects of data analysis, manipulation, and reporting.
These features are designed to streamline the analytical process, enhance user experience, and deliver actionable insights. Below, we explore some of the key functionalities that make SAS a preferred choice for business intelligence.
Key Features Relevant to Business Intelligence
The following features underscore the significance of SAS in business intelligence analytics. Each feature plays a critical role in facilitating data-driven decision-making processes.
- Advanced Analytics: SAS offers advanced statistical analysis techniques, including predictive modeling, machine learning, and data mining, enabling organizations to uncover hidden patterns and trends.
- Data Integration: The platform provides robust data integration capabilities, allowing users to access, blend, and analyze data from various sources seamlessly.
- Visual Analytics: SAS includes powerful visualization tools that help in creating interactive dashboards and reports, making data more accessible and understandable.
- Scalability: SAS is designed to handle large volumes of data efficiently, ensuring that businesses can scale their analytics efforts as needed without compromising performance.
- User-Friendly Interface: With its intuitive interface, SAS enables users of varying skill levels to navigate and utilize its capabilities effectively.
Comparison of SAS Features with Competitors
The following table presents a comparative analysis of SAS features against some of its key competitors in the business intelligence domain. This comparison highlights SAS’s distinct advantages and areas where it excels.
| Feature | SAS | Competitor A | Competitor B |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Analytics | Yes | Limited | Yes |
| Data Integration | Comprehensive | Moderate | Basic |
| Visual Analytics | High | Medium | High |
| Scalability | Excellent | Average | Good |
| User-Friendly Interface | Intuitive | Complex | Moderate |
Functionalities for Data Manipulation and Reporting
SAS provides an array of functionalities that enhance data manipulation and reporting capabilities, essential for businesses aiming to derive meaningful insights from their data. These functionalities include:
Data Preparation
SAS offers tools for data cleaning, transformation, and preparation. This ensures that data is of high quality and ready for analysis. Through features like data profiling and validation, users can identify anomalies and rectify them effectively.
Reporting Tools
With SAS, users can generate comprehensive reports that summarize findings and visualize data trends. The reporting features allow for flexibility in format, catering to various stakeholder needs.
Automated Workflows
The automation capabilities in SAS streamline routine tasks, reducing manual effort and minimizing errors. This is particularly beneficial in large-scale data processing scenarios.
Collaboration Features
SAS supports collaboration among team members through shared projects and dashboards, facilitating effective communication and collective decision-making.
Real-time Analytics
The platform’s real-time analytics capabilities enable businesses to react to emerging trends and changes in data promptly, fostering agility and responsiveness in strategy formulation.
The effectiveness of SAS in business intelligence analytics is demonstrated by its capacity to integrate complex data sets, deliver real-time insights, and enhance organizational decision-making.
Implementation Strategies for SAS in Organizations: Benefits Of Using SAS For Business Intelligence Analytics.
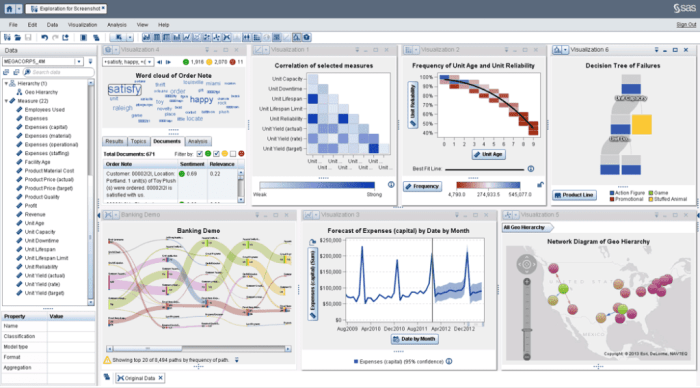
Implementing SAS in an organization involves a systematic approach that ensures effective integration into existing operations. A well-defined strategy enhances the likelihood of successful adoption, maximizes the potential benefits, and facilitates a smooth transition for users. This section Artikels key steps to take when implementing SAS, best practices for training personnel, and methods to evaluate the system’s effectiveness after deployment.
Step-by-Step Guide for Implementing SAS
A structured implementation strategy is critical for organizations aiming to leverage SAS for business intelligence analytics. Following these steps can streamline the process and mitigate potential challenges:
- Assessment of Needs: Conduct an assessment of the organization’s data analytics needs, current capabilities, and desired outcomes with SAS.
- Define Objectives: Set clear objectives for what the organization aims to achieve with SAS, aligning them with broader business goals.
- Project Planning: Develop a detailed project plan outlining timelines, resources required, and key milestones for implementation.
- Infrastructure Setup: Prepare the necessary IT infrastructure, ensuring that hardware and software requirements for SAS are met.
- Data Integration: Integrate existing data sources into SAS, ensuring that data quality and accessibility are prioritized.
- System Configuration: Configure SAS according to the organization’s specific needs, including customizing features and functionalities.
- Testing Phase: Conduct thorough testing of the SAS system to identify and rectify any issues before full deployment.
- Launch: Officially launch SAS within the organization, ensuring all teams are aware of its availability and purpose.
- Post-Implementation Support: Provide ongoing support and maintenance to address any unforeseen challenges and ensure optimal performance.
Best Practices for Training Employees on SAS
Effective training is crucial for maximizing the benefits of SAS. Implementing best practices in training ensures that employees are well-equipped to utilize the platform efficiently:
“Investing in training leads to greater satisfaction and productivity among users.”
Organizations should consider the following best practices:
- Comprehensive Training Programs: Develop structured training programs that cover all key functionalities of SAS, tailored to different user roles.
- Hands-On Workshops: Incorporate hands-on workshops where employees can practice using SAS with real datasets to reinforce learning.
- Ongoing Learning Opportunities: Offer continuous learning resources, such as online courses and tutorials, to keep employees updated on new features.
- Mentorship and Support: Pair less experienced users with SAS experts within the organization to foster a culture of learning and support.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Implement feedback mechanisms to assess the effectiveness of training programs and make necessary adjustments.
Evaluation of SAS Effectiveness Post-Implementation
Post-implementation evaluation is vital in determining the success of SAS and identifying areas for improvement. Organizations can employ the following methods to assess effectiveness:
“A systematic evaluation process ensures the continuous alignment of SAS with business objectives.”
Evaluation can be conducted through:
- Performance Metrics: Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the impact of SAS on analytics efficiency and decision-making.
- User Feedback Surveys: Distribute surveys among users to gather insights on their experience with SAS and any challenges faced.
- Usage Analytics: Analyze user engagement and frequency of usage to assess how well SAS is being adopted across the organization.
- Return on Investment (ROI) Analysis: Conduct an ROI analysis to measure the financial benefits gained from using SAS against the costs incurred.
- Regular Review Meetings: Schedule regular meetings to discuss findings with stakeholders and identify ongoing improvements or necessary adjustments.